C++对象模型--多继承
C++对象模型--多继承
1. 多继承–无虚拟继承
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
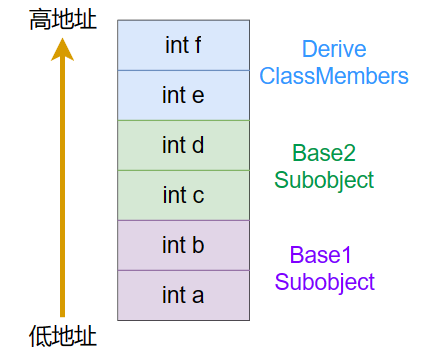
class Base1 {
public:
int a;
int b;
};
class Base2 {
public:
int c;
int d;
};
class Derive : public Base1 , public Base2 {
public:
int e;
int f;
};
内存布局顺序为:Base1的成员变量 -> Base2的成员变量 -> Derive的成员变量。如下图所示(图中一格表示4字节):
1.1 指针调整
当进行Derive / Base 指针赋值或比较时,编译器对Base / Derive 指针进行偏移调整。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
int main() {
Derive* d_ptr = new Derive();
Base2* b2_ptr = d_ptr;
Base1* b1_ptr = d_ptr;
printf("address of d_ptr = %p\n", d_ptr);
printf("address of b1_ptr = %p\n", b1_ptr);
printf("address of b2_ptr = %p\n", b2_ptr); // 指针调整
if (d_ptr == b2_ptr) { // 明明两个指针在数值上不相同,但从C++的语义上看,两个指针指向同一个对象,所以编译器还是进行指针调整。
printf("d_ptr == b2_ptr\n");
}
if (d_ptr == b1_ptr) {
printf("d_ptr == b1_ptr\n");
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
address of d_ptr = 0x560982eebe70
address of b1_ptr = 0x560982eebe70
address of b2_ptr = 0x560982eebe78
d_ptr == b2_ptr
d_ptr == b1_ptr
参考
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权