聚类算法(密度):基于 nano-flann
聚类算法(密度):基于 nano-flann
0. DBSCAN 算法及 K-D 树介绍
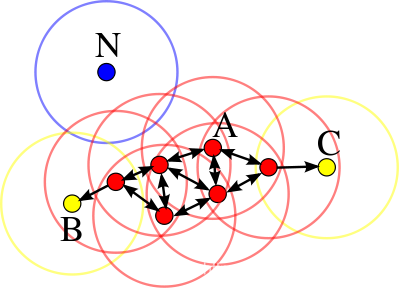
DBSCAN算法相关概念:
- 邻域半径
eps。 - 核心点,最少核心点
minPts。 - 直接密度可达。
- 密度可达。
- 密度相连。
K-D树的时间复杂度:
Kdtree 算法的构建时间复杂度为 O(nlogn),搜索时间复杂度最好为 O($\log_2 N$),最坏为 O($N^{1-1/k}$)。
1. 背景
采集到的二维点云数据(samples),生成K-D搜索树,使用广度优先搜索,聚合成block数据。后续的识别/分类算法,在block数据基础上进行。
由于使用点云处理库PCL比较庞大,以及其依的FLANN基于C++14,使用C++17/20导致在自定义点云数据结构时,编译有些STL算法库被废弃,编译出错。故使用 nanoflann。
2. 基于 nano-flann 的聚类算法实现
2.1 自定义点云数据结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
#pragma once
// test\test_flann\flann_adaptor.h
#include <vector>
#include "3rd_utils.h"
#include "typedef.h"
struct PointCloud {
using Point = rias::data_type::sample_data_t;
using coord_t = double; //!< The type of each coordinate
std::vector<Point> pts;
// Must return the number of data points
inline size_t kdtree_get_point_count() const { return pts.size(); }
// Returns the dim'th component of the idx'th point in the class:
// Since this is inlined and the "dim" argument is typically an immediate
// value, the
// "if/else's" are actually solved at compile time.
inline double kdtree_get_pt(const size_t idx, const size_t dim) const {
CHECK2(dim < 2, "Invalid dimension: " << dim);
if (dim == 0) return pts[idx].mapped_pos_.x_;
else return pts[idx].mapped_pos_.y_;
}
// Optional bounding-box computation: return false to default to a standard
// bbox computation loop.
// Return true if the BBOX was already computed by the class and returned
// in "bb" so it can be avoided to redo it again. Look at bb.size() to
// find out the expected dimensionality (e.g. 2 or 3 for point clouds)
template <class BBOX>
bool kdtree_get_bbox(BBOX& /* bb */) const {
return false;
}
};
2.2 基于 K-D 树构建广度优先搜索算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
#pragma once
// test\test_flann\point_cloud_algorithm.h
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#pragma warning(push)
#pragma warning(disable : 4267) // disable conversion warning
#include "nanoflann/nanoflann.hpp"
#pragma warning(pop)
#include "3rd_utils.h"
#include "flann_adaptor.h"
#include "typedef.h"
namespace rias::test {
class BFSDensitySampleSearch {
static constexpr int32_t kDIM = 2;
using my_kd_tree_t = nanoflann::KDTreeSingleIndexAdaptor<nanoflann::L2_Simple_Adaptor<double, PointCloud>, PointCloud, kDIM>;
using sample_t = rias::data_type::sample_data_t;
public:
BFSDensitySampleSearch(const std::vector<sample_t>& pts) : pts_(pts) {}
~BFSDensitySampleSearch() = default;
BFSDensitySampleSearch& setRadius(double radius) {
radius_ = radius;
return *this;
}
BFSDensitySampleSearch& setMinPts(double minPts) {
minPts_ = minPts;
return *this;
}
const std::vector<std::vector<size_t>>& clusters() const { return clusters_; }
BFSDensitySampleSearch& search() {
PointCloud cloud;
cloud.pts = pts_;
CHECK1(sizeof(double[kDIM]) == sizeof(data_type::point_double_t), "sizeof(double[kDIM])");
my_kd_tree_t index(kDIM /*dim*/, cloud, {10 /* max leaf */});
std::vector<double> densities(pts_.size(), double{});
for (size_t i = 0; i < pts_.size(); i++) {
const auto* q_pt = (double*)(&pts_[i].mapped_pos_);
std::vector<nanoflann::ResultItem<uint32_t, double>> ret_matches;
const size_t n_matched = index.radiusSearch(q_pt, radius_, ret_matches);
densities[i] = static_cast<double>(n_matched);
}
std::vector<bool> visited(pts_.size(), false);
for (size_t i = 0; i < pts_.size(); i++) {
if (visited[i] /*|| densities[i] < minPts_*/) { // 0. skip visited or low density points
continue;
}
std::vector<size_t> cluster;
std::queue<size_t> q;
q.push(i); // 1. add self ot queue at first
visited[i] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
const auto idx = q.front();
q.pop();
cluster.push_back(idx); // 2. elements in the same queue are in the same cluster
const auto* q_pt = (double*)(&pts_[idx].mapped_pos_);
std::vector<nanoflann::ResultItem<uint32_t, double>> ret_matches;
const size_t n_matched = index.radiusSearch(q_pt, radius_, ret_matches);
for (size_t j = 0; j < n_matched; j++) { // 3. add matched points to the same queue
const auto n_idx = ret_matches[j].first;
// const auto n_dist = ret_matches[j].second;
if (!visited[n_idx] && densities[n_idx] >= minPts_) {
visited[n_idx] = true;
q.push(n_idx);
}
}
}
// 4. a cluster done (one or more points)
clusters_.push_back(cluster);
}
return *this;
}
private:
const std::vector<sample_t>& pts_;
double radius_{1.0}, minPts_{1.0};
std::vector<std::vector<size_t>> clusters_;
};
} // namespace rias::test
2.3 测试代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
{
const auto t0 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto dss = BFSDensitySampleSearch(sample_ds->ds_).setRadius(3.0).setMinPts(1.0);
auto clusters = dss.search().clusters();
const auto t1 = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
const auto dur = std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>(t1 - t0).count();
spdlog::info("search in {} points. found {} clusters. time: {:.3f} seconds\n", sample_ds->ds_.size(), clusters.size(),
dur / 1000.0);
/*for (const auto& cluster : clusters) {
//spdlog::info("{}", fmt::join(cluster, ", "));
spdlog::info("cluster: {}", cluster);
}*/
}
2.4 测试
1
2
3
4
[2024-08-26 21:47:35.648] [warning] [dataxy_loader.cc:146] under flow 870 samples in dataset
[2024-08-26 21:47:35.649] [info] load data from file: 0.37393689999999996 seconds
[2024-08-26 21:47:37.740] [info] search in 1503894 points. found 438931 clusters. time: 2.133 seconds
TODO: 测试小数据集下的性能对比。
2.5 参考
3. 基于templated的聚类算法实现(线性搜索 O2时间复杂度)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
template <typename ElemType, typename LinerFuncType, typename AdjFuncType>
class BFSLinerMerge {
public:
BFSLinerMerge(const std::vector<ElemType>& blocks, LinerFuncType linerCondFunc, AdjFuncType adjCondFunc)
: blocks_(blocks), liner_cond_func_(linerCondFunc), adj_cond_func_(adjCondFunc) {};
BFSLinerMerge& search() {
if (!clusters_.empty()) clusters_.clear();
std::vector<bool> visited(blocks_.size(), false);
clusters_.reserve(blocks_.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < blocks_.size(); i++) {
if (visited[i]) continue;
std::queue<size_t> q;
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;
std::vector<Block*> cluster;
while (!q.empty()) {
size_t idx = q.front();
q.pop();
const auto this_blk = blocks_[idx];
cluster.push_back(blocks_[idx]);
for (size_t j = 0; j < blocks_.size(); j++) {
if (visited[j]) continue;
const auto& blkj = blocks_[j];
if (liner_cond_func_(this_blk, blkj) && adj_cond_func_(this_blk, blkj)) {
q.push(j);
visited[j] = true;
}
}
}
clusters_.push_back(cluster);
};
return *this;
}
std::vector<std::vector<ElemType>>& clusters() { return clusters_; }
private:
const std::vector<ElemType>& blocks_;
LinerFuncType liner_cond_func_;
AdjFuncType adj_cond_func_;
std::vector<std::vector<ElemType>> clusters_;
};
4. 聚类算法资料收集
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权