std::shared_ptr 线程安全及性能考量
std::shared_ptr 线程安全及性能考量
1. 线程安全
根据cppreference的描述,std::shared_ptr线程安全如下(机器翻译):
- 如果是每个线程都拥有自己的
std::shared_ptr对象,则针对线程自己的std::shared_ptr对象,其所有成员函数都是线程安全的; - 如果多个线程共享同一个
std::shared_ptr对象,其const成员函数的访问是线程安全的,但其非const成员函数的访问需要同步。 - 多线程访问同一个
std::shared_ptr对象时,使用std::atomic<std::shared_ptr<T>>可以防止数据竞争。
原文:
All member functions (including copy constructor and copy assignment) can be called by multiple threads on different shared_ptr objects without additional synchronization even if these objects are copies and share ownership of the same object. If multiple threads of execution access the same shared_ptr object without synchronization and any of those accesses uses a non-const member function of shared_ptr then a data race will occur; the std::atomic
总结:
- 多线程拷贝同一个
std::shared_ptr对象,是线程安全的(引用计数是线程安全的)。 - 多线程访问
std::shared_ptr指向的同一个内存对象时,访问const成员函数是线程安全的。 - 其余情况,需要使用同步。
2. 性能考量
- 使用
std::make_shared,std::make_shared将被指向对象的内存分配与控制块的内存分配合并为一次分配; std::make_shared的性能接近new;但std::shared_ptr<T>(new T)耗时较明显;- 在
x86平台,std::shared_ptr的访问时间应该接近T*;但ARM平台应该会有明显的性能差异;
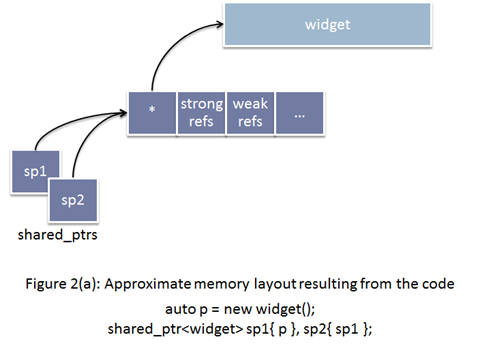
使用原始指针并赋值给shared_ptr,shared_ptr管理对象与控制块内存布局:
而使用std::make_shared,shared_ptr管理对象与控制块内存布局:
3. 更多资料
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权